Team E - Induino Garden

Final Presentation Download
The Problem:
For people that don’t have any type of outdoor growing area or a climate that does not support the growth of the plants, it is hard to grow anything when you don’t have the proper tools or the right environment because the plants might need a specific type of environment to grow properly.
The Solution:
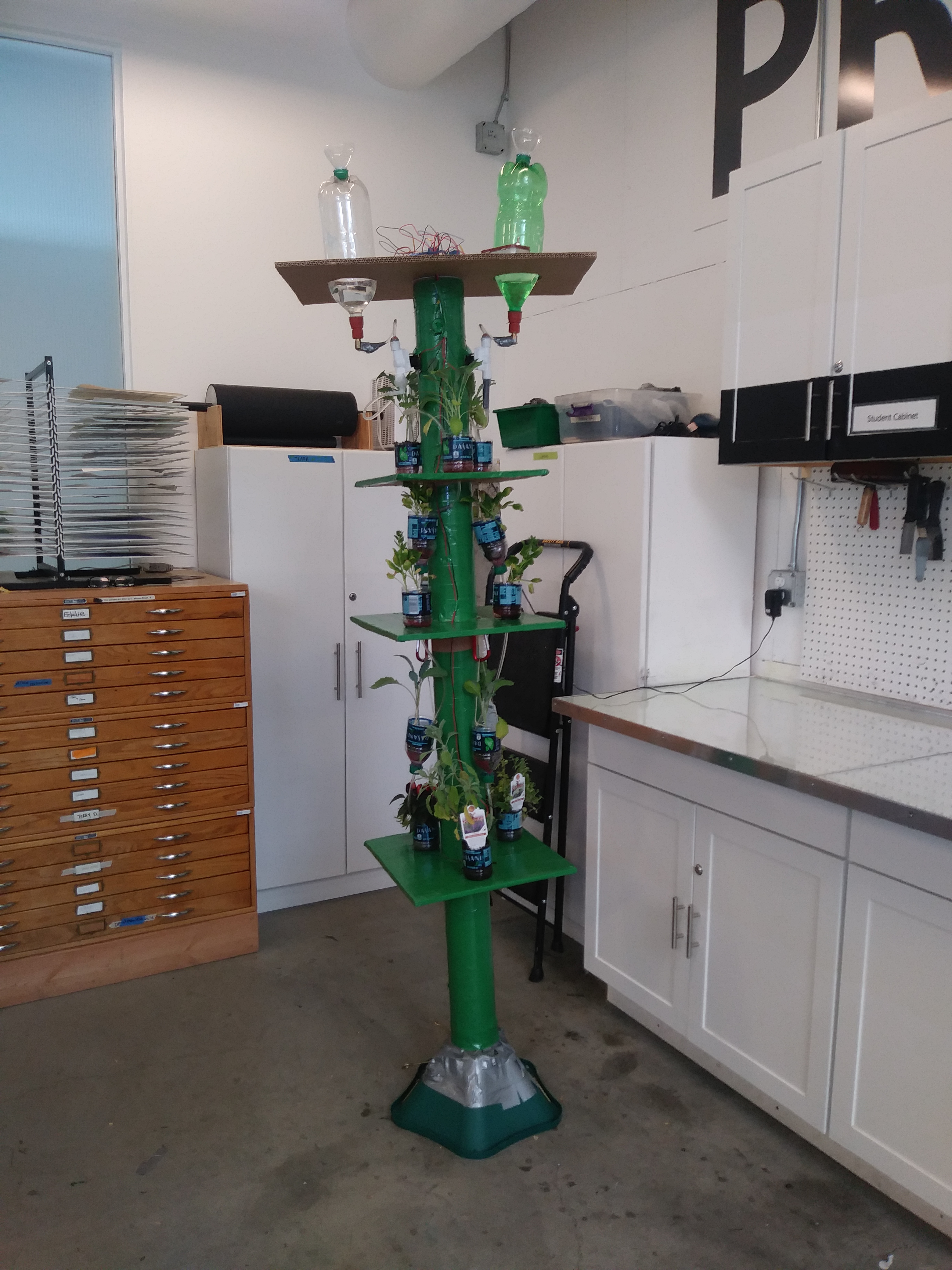
An invention to address this problem would be an indoor vertical garden that is able to monitor PH levels and moisture, and it would have a self automated watering and fertilizing system. It would also be sustainable and made of recycled materials. The Induino Garden will include 10-15 planting sections with self automated watering systems. We would love to make a vertical and mobile design because that would make it easier to move and it would take up less space. We would like a model that is affordable, so we will try to incorporate as much recycled materials as possible. If we have enough time, we will like to include a PH level monitor as well.This invention would be called the Induino Garden.
Possible Users/Customers:
- People that don’t have access to a garden outside
- People who’s soil isn’t good for planting
- Someone that doesn’t have a good climate for growing outside
- Low income/food insecurity
- People who need to de-stress
Invention Attributes:
Minimum Requirements:
- 10-15 sections for planting
- Automated watering system
- Liquid Fertilizer
- Affordable
Secondary Goals:
- A vertical design
- Mobile
- Uses Recycled Materials
Reach Goals:
- A PH level monitor
History and Context:
PLANTS - thyme, basil, mint, oregano, cilantro, lemon balm, kale, lettuce, scallions, arugula, spinach, sage
__ Hydroponics plants and how they work!__
Hydroponics is a branch of agriculture where plants are grown without the use of soil. The nutrients that the plants normally derive from the soil are simply dissolved into water instead, and depending on the type of hydroponic system used, the plant’s roots are suspended in, flooded with or misted with the nutrient solution so that the plant can derive the elements it needs for growth.
Hydroponically growing plants isn’t a new method, it can be dated back the Aztecs and babylonians. The babylonians used the hydroponic method to water their famous Hanging Gardens, which grew in a humid climate with little rain. And the Aztecs, when unable to grow their crops on the marshy shores of the Lake Tenochtitlan, they put their crops on rafts and grew them on the lake. Both instances of hydroponic gardening, while crude, show the beginnings of water-growing. Centuries later, scientists began to experiment in hydroponic growing. People like Francis Bacon, John Woodward, and William Gericke all made progress in popularizing the idea of growing plants hydroponically.
http://www.fullbloomhydroponics.net/hydroponic-systems-101/ https://home.howstuffworks.com/lawn-garden/professional-landscaping/hydroponics1.htm
Regular soil plants:
Nutrients in the soil also help plants grow strong. Some nutrients that plants need are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. … This limits their access to soil nutrients and weakens the plant’s hold in the ground.
https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/how-do-seeds-sprout/
HOW PLANTING HELPS OUR MENTAL HEALTH!!
Planting your own garden or plants gives us a sense of responsibility, where it is up to us to take care and maintain the the life of the plant. Gardening also allows us to be nurturers and participating in a very transformative activity can boost self-esteem!
Gardening also is a gentle reminder that we aren’t the only ones and self-absorption can lead to depression. For many the peacefulness associated with gardening comes not from its social aspect however, but the opposite. It enables us to escape from other people which can relieve stress.They say that gardening encourages us to exercise and spend time outdoors which might seem obvious, but it’s worth reminding ourselves that what’s good for the body is also good for the mind.
[https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/worry-and-panic/201505/petal-power-why-is-gardening-so-good-our-mental-health]
SOCIAL CONTEXT:
The Induino Garden may be able to help food insecurity because it is cheaper and it can be used to grow edible plants. It can help to improve air quality through the plants, as well. In fact, NASA research has shown that houseplants can remove up to 87% of air toxin in 24 hours. Also, studies have shown that having a plant in one’s home can improve concentration and productivity, reduce stress levels, and boost one’s mood.
RESEARCH DESIGN: (TECH/SENSORS/TOOLS)
SENSORS:
-
SOLENOID VALVE: It is nothing more than a valve controlled by an electromagnet. It is, like relays and motors, an inductive load. They usually come in two types, Normally Open or Normally Closed. Normally refers to when-there-is-no-current-in-the-solenoid. If you put pressurized water in a NC (Normally Closed) solenoid valve, water will be blocked. If you power the magnet with the expected current / voltage, the valve will open and the water will flow. https://www.instructables.com/id/Controling-a-solenoid-valve-with-an-Arduino/
-
PH MONITOR: PH sensors are used to test the acidity or alkalinity of liquids. PH probes are like batteries with high resistance. The voltage output is equivalent to the Hydrogen Ion concentrated around the probe. The voltage will be +/- depending on whether the liquid is alkaline or acidic. The probe contains two electrodes, one covered with KCl (Potassium Chloride) and HCl (Hydrogen Chloride). The HCl electrode is covered in a glass bulb, which only allows Na (Sodium) to pass through. The KCl electrode acts as a reference for the PH level. PH sensors use the hydrogen ions to sense the PH levels. When the NaCl passes through the bulb, it’s stripped of its hydrogen ions. Which allows the sensor to measure the PH. https://www.sparkyswidgets.com/portfolio-item/ph-probe-interface/
- HUMIDITY TEMP SENSOR
- MOISTURE SENSOR
TOOLS
We will use many different tools when building the Induino Garden.
- LASER CUTTER: We will use a laser cutter to cut discs to put on the rod. These discs will hold the water bottle pots.
- 3D PRINTER: We will use a 3D printer to print hooks for the top of the rod. These hooks will hold the hanging water bottle pots up.
We will use simpler tools as well, such as a glue gun, scissors, ruler, and Xacto knife.
- GLUE GUN: The glue gun will be used to glue the hooks and discs onto the rod. It will also be used to glue the water bottle pots onto the discs.
- SCISSORS: The scissors will be used to cut string, which will be used to hold if the hanging water bottle pots.
- RULER: The ruler will be used to measure the string before it is cut.
- XACTO KNIFE: The Xacto knife will be used to cut the bottom or top off of the water bottles.
Design Ideas:
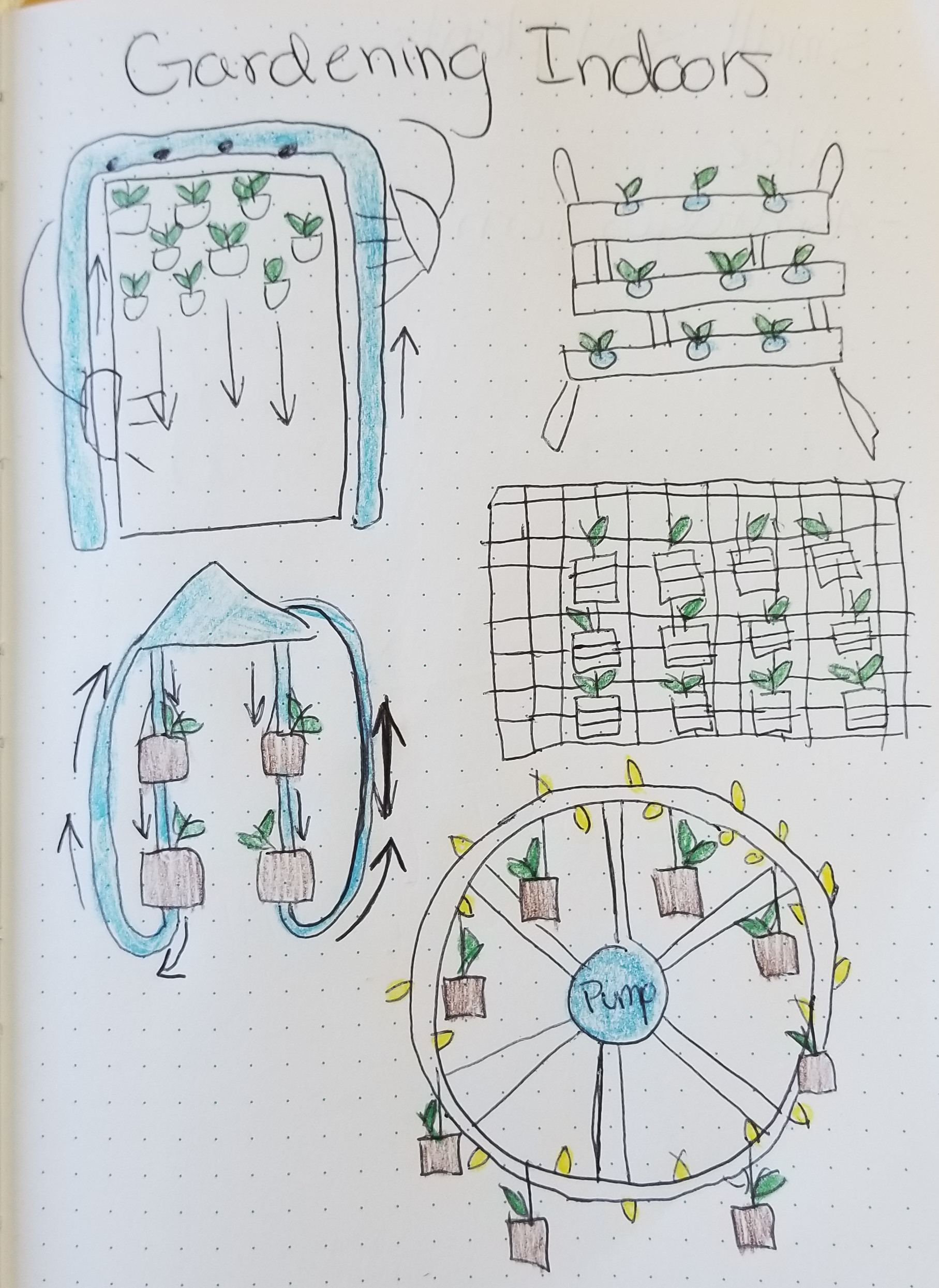
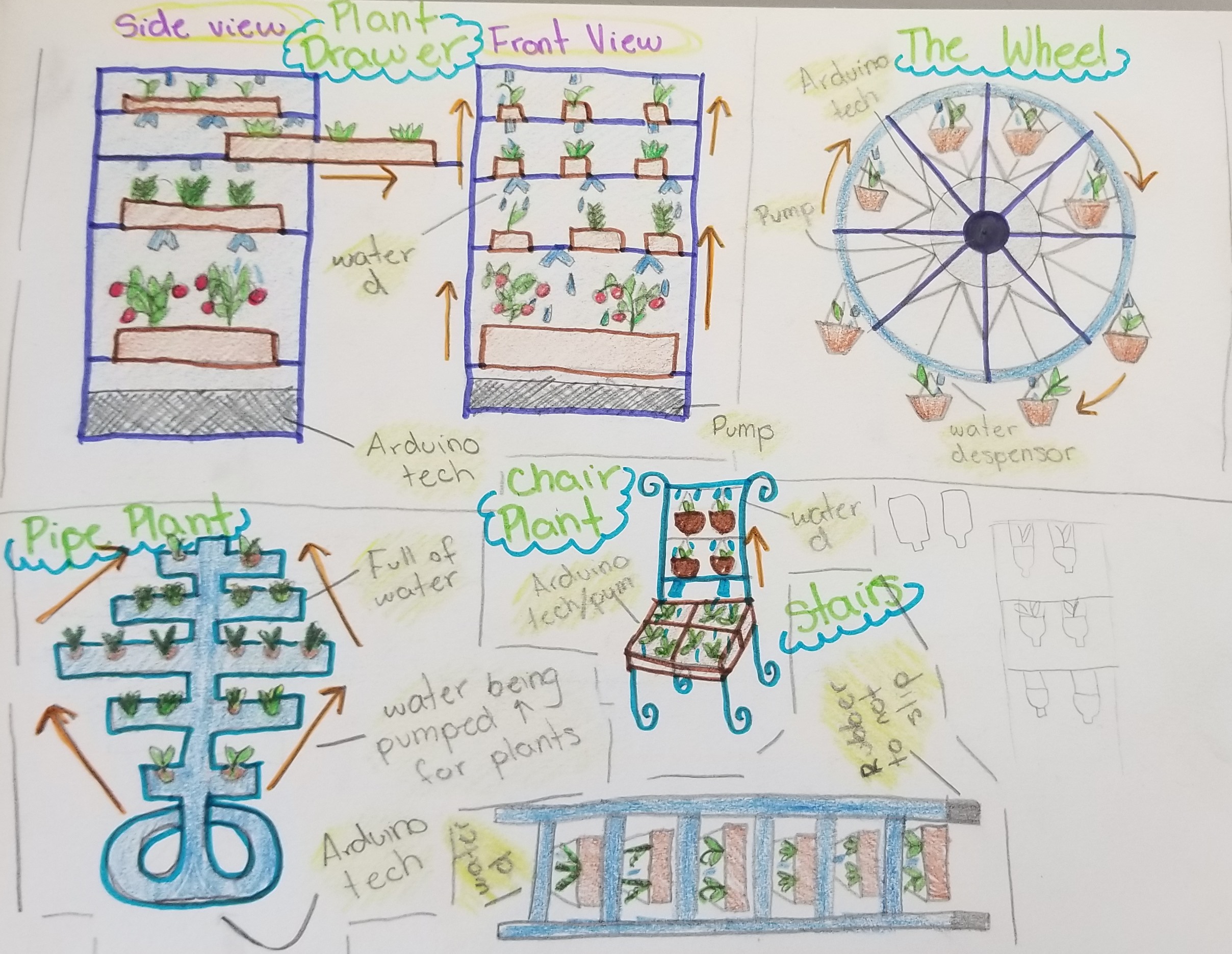
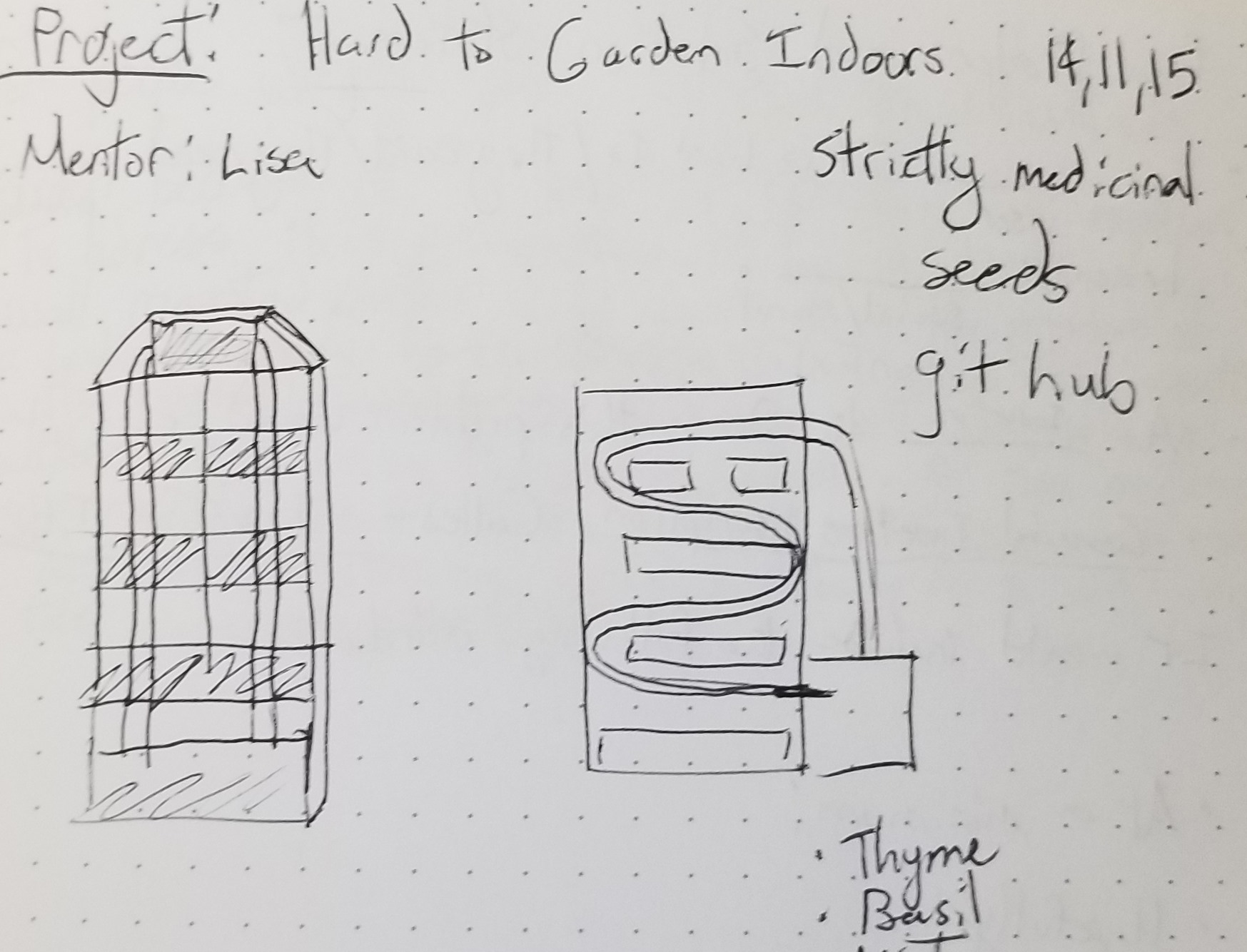
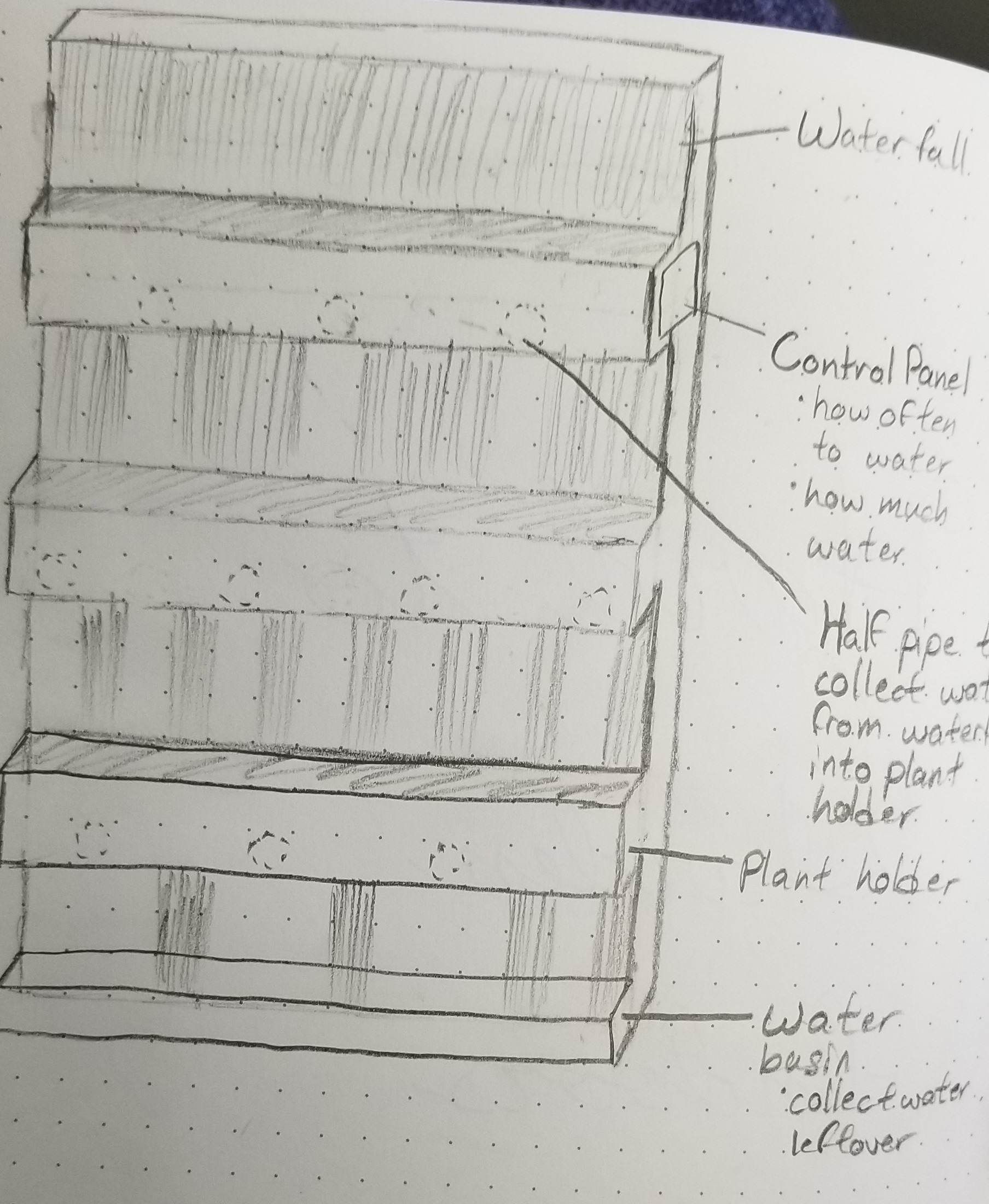
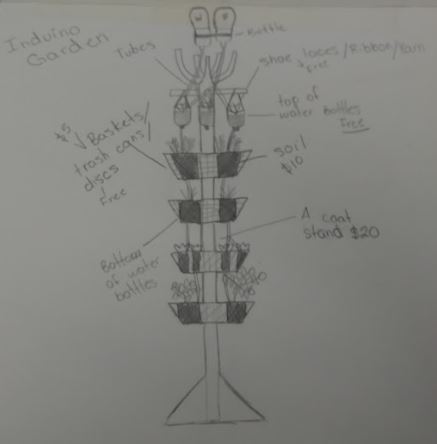
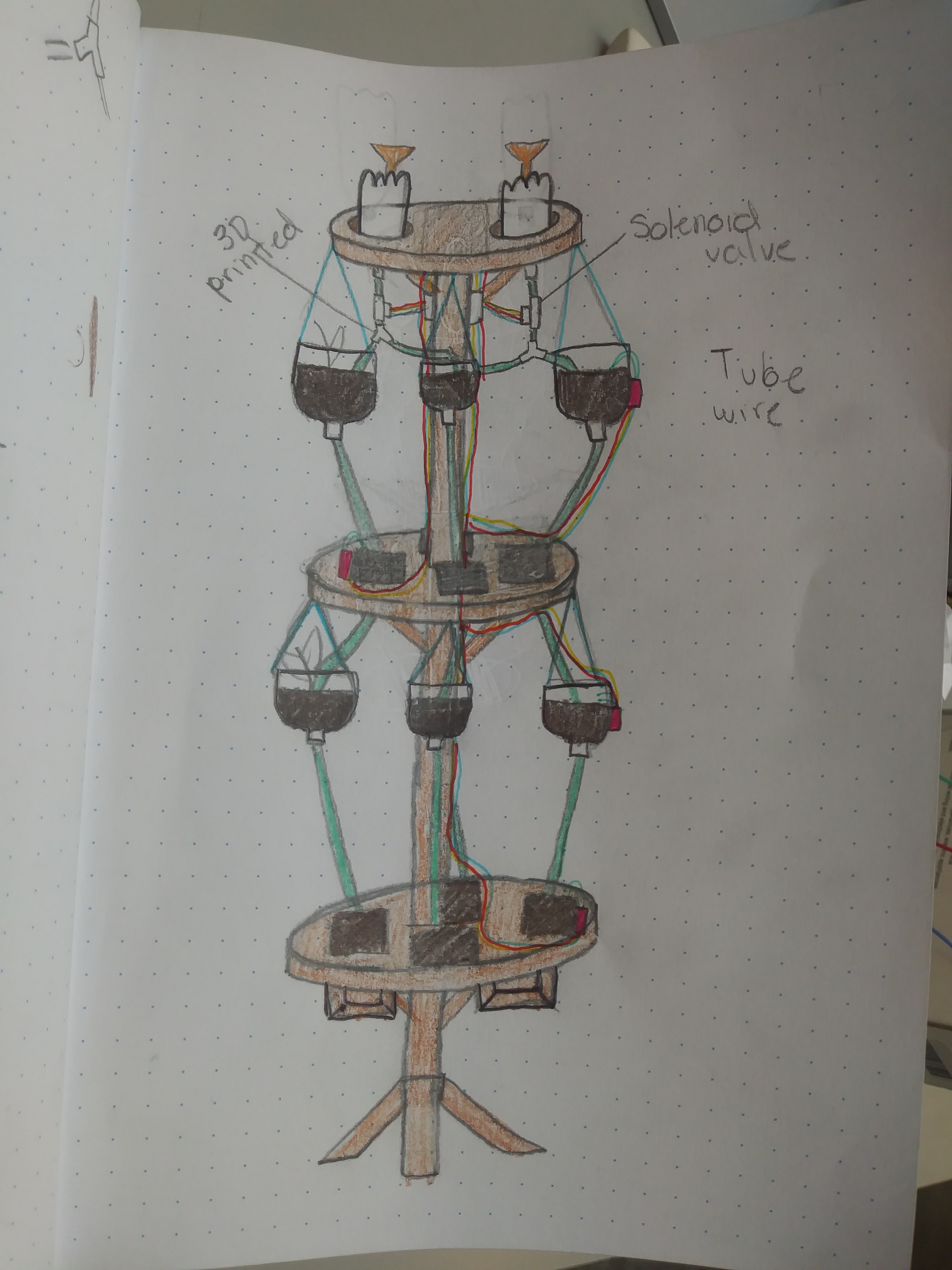
Subsystem Map:
- Electrical Lead: Annabelle Hauss
- How will we measure when the plants need more water?
- Moisture Sensor
- Will moisture sensors be placed in each pot, a few pots, or one?
- A few pots, one on each level
- What will the LCD screen show?
- When water level is low
- The ph (if we have time) -The temperature (if we have time)
- Do we want it to plug into a wall of have a battery?
- Plug into wall
- How much power is needed for the Induino Garden to function?
- How much power does each component require?
- Moisture sensor: 3-5 V *4
- Ph sensor: 3 V *4
- Solenoid valve: 12 V *2
- How much power is that in total?
- Where will we run the wires?
- Along the pole/rod for the sensors in the pots
- The rest of the wiring will be at the top with the Arduino
- How will we measure the ph level of the soil? (if we have time)
- Ph sensor
- Will ph sensors be placed in each pot, a few pots, or one?
- A few
- How will we stop and start the flow of fertilizer and water?
- Solenoid Valves
- How will we measure when the plants need more water?
- Materials - Electric:
- Solenoid Valve *2
- About 15 feet of wire total
- LCD Screen
- Ph Sensor
- Resistors (for moisture sensor)
- Arduino
- Mechanical Lead: Ana Acevedo
- How tall do we need our structure to be?
- Where do we locate the motors/ Arduinos and how big are they?
- What is the width of the pots to plant on/discs?
- How long will the tubbing need to be to have all the plants connected and what width should they be?
- How many planting sections will we have/need?
- Programming Lead- Emma
- How do we open the solenoid valve?
- How do we measure the temperature and humidity?(Are we measuring temp/humidity?) No
- How/Where do we put the PH sensors? Only if there’s time
- What will the LCD screen be showing?(Water levels)
- How will we track the levels of water and fertilizers in the bottle?
- How will we measure moisture levels, and how will we make it open the solenoid valve? 4 moisture sensors
BOM (Bill of Materials):
Materials:
- Wood - ~$22
- 2 Rods: 4in x 4in x 8 ft
- Water Bottles - $0
- Tubes - $
- Soil - $5
- String - $0
- 2 solenoid valve - $15 each
- About 15 feet of wire total - $0
- LCD Screen - $
- Ph Sensor - $… cheaper than 40 doesn’t exist
- Resistors (for moisture sensor) - $0
- Arduino - $0
- Nails - $
- Plants - $
- Fertilizer - $
- 4 Wheels - $
Final Product:

- Mobile
- Self automated watering system
- Holds 15 plants
- Uses recycled materials